Navigation
- Change Log
- VPX Hardware – VMXNET3
- Customer User Experience Improvement Program (CUXIP)
- Welcome Wizard
- Licensing:
- Upgrade Firmware
- High Availability
- Networking
- DNS Servers
- NTP Servers
- Syslog Server
- SNMP Configuration
- Call Home
- Change nsroot password
- TCP, HTTP, SSL, and Security settings
- LDAP Authentication for Management
- CLI Prompt
- Backup and Restore
💡 = Recently Updated
Change Log
- 2018 Feb 8 – in TCP Settings section, added info from Citrix CTX232321 Recommended TCP Profile Settings for Full Tunnel VPN/ICAProxy from NetScaler Gateway 11.1 Onwards
- 2017 Dec 14 – in Dedicated Mgmt section, added config for floating mgmt IP
VPX Hardware
NetScaler VPX Release 11.1 supports new VPX models on ESXi. These new models include: VPX 25, VPX 5G, VPX 25G, etc. See the NetScaler VPX datasheet for more info.
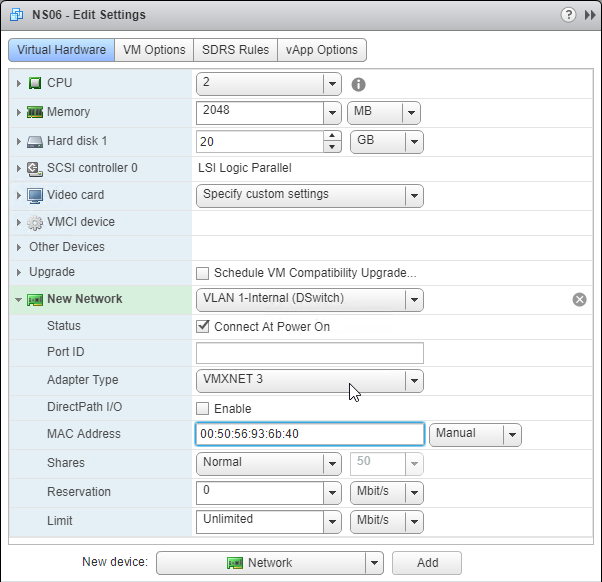
NetScaler VPX Release 11.1 also supports changing the NIC type to VMXNET3 or SR-IOV. The imported appliance comes with E1000 NICs so you’ll have to remove all of the existing virtual NICs and add new VMXNET3 NICs.
- Citrix CTX224576 NetScaler VPX Loses Network Connectivity Intermittently on VMware ESXi After Upgrading to Version 12.0 recommends VMXNET3 as a workaround to network connectivity issues in recent 11.0, 11.1, and 12.0 builds.
- If you choose to use VMXNET3 instead of E1000, make sure all of the NICs are VMXNET3. You cannot mix NIC types.
- If you already licensed your appliance, jot down the E1000 MAC address, and configure the new VMXNET3 NIC with the same MAC address.
Power On VPX and configure NSIP
- After swapping out the NICs to VMXNET3, power on the NetScaler VPX appliance.

- Configure the management IP from the VM’s console.

- Then point your browser to the management IP using either http or https and login as nsroot with password nsroot.

Auto-Provision IP Address
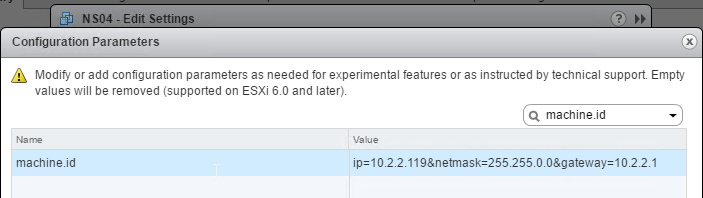
When importing VPX into a hypervisor, you can use VM advanced configuration parameters to set the NSIP. See CTX128250 How to Auto-Provision NetScaler VPX Appliance on a VMware ESX or ESXi Host, and CTX128236 How To Auto-Provision NetScaler VPX on XenServer.
Customer User Experience Improvement Program
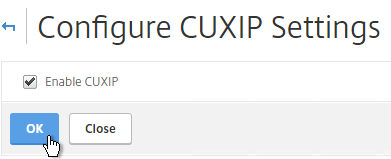
- You might be prompted to enable the Customer User Experience Improvement Program. Either click Enable, or click Skip.


- You can also enable or disable the Customer Experience Improvement Program by going to System > Settings.
- On the right is Change CUXIP Settings.
- Make your selection and click OK.
- See https://www.carlstalhood.com/delivery-controller-7-15-ltsr-and-licensing/#ceip for additional places where CEIP is enabled.
set system parameter -doppler ENABLED
Welcome Wizard
NetScaler has a Welcome! Wizard that lets you set the NSIP, hostname, DNS, licensing, etc. It appears automatically the first time you login.
- Click the Subnet IP Address box.
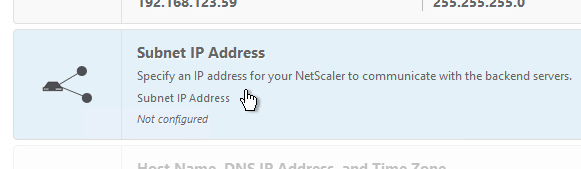
- You can either enter a SNIP for one of your production interfaces, or you can click Do it later, and add SNIPs later after you configure Port Channels and VLANs. Note: If you have a dedicated management network, to prevent it from being used for outgoing traffic, don’t put a SNIP on it.
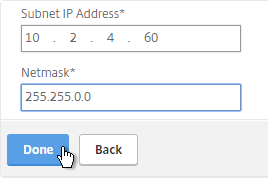
add ns ip 10.2.2.60 255.255.255.0 -type SNIP
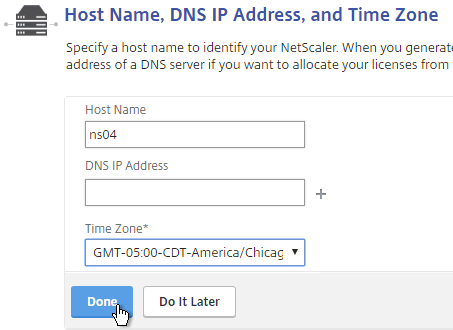
- Click the Host Name, DNS IP Address, and Time Zone box.
- Enter a hostname. Your NetScaler Gateway Universal licenses are allocated to this hostname. In a High Availability pair each node can have a different hostname. You typically create a DNS record that resolves the hostname to the NSIP (management IP).
- Enter one or more DNS Server IP addresses. Use the plus icon on the right to add more servers.
- Change the time zone to GMT-05:00-CDT-America/Chicago or similar.
- Click Done.
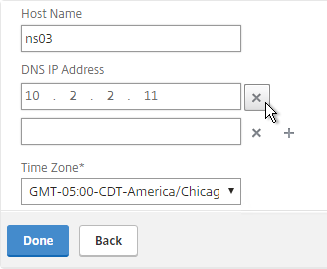
set ns hostname ns02 add dns nameServer 10.2.2.11 set ns param -timezone "GMT-05:00-CDT-America/Chicago"
- Click Yes to save and reboot.
- Click the Licenses box.
- On the far right side of the screen, you’ll see the Host ID. You’ll need this to allocate your licenses at citrix.com. See below for detailed instructions on how to allocate the license to this Host ID.

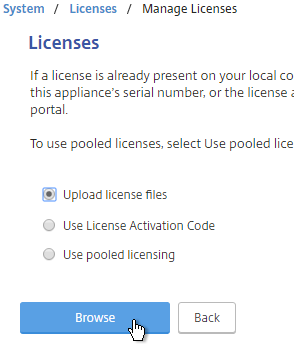
- On the left, select Upload license files, and click Browse.

- Browse to the license file, open it, and click Reboot when prompted.

- After the reboot and logging in, a box will pop up showing you the installed license.

- Also look in the top left corner to make sure it doesn’t say NetScaler VPX (1). The number in the parentheses should match the MPX or VPX model number.
 License files are stored in /nsconfig/license.
License files are stored in /nsconfig/license.
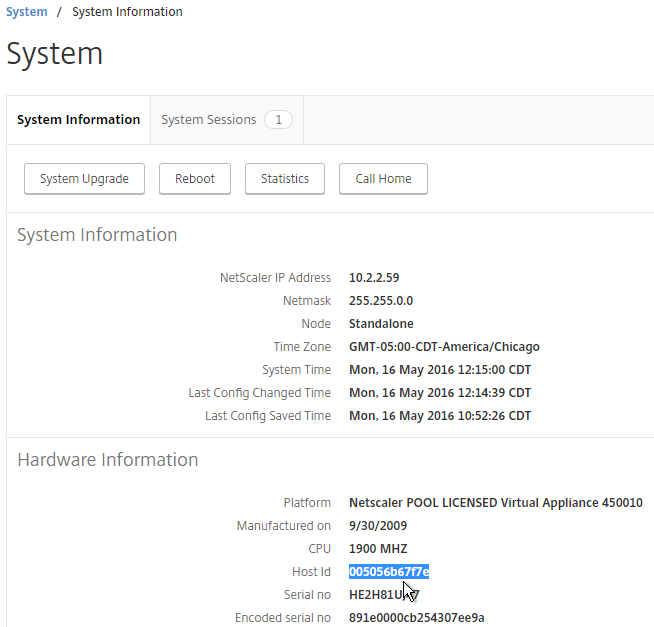
Licensing – VPX Mac Address
To license a NetScaler VPX appliance, you will need its MAC address.
- Go to the Configuration tab.
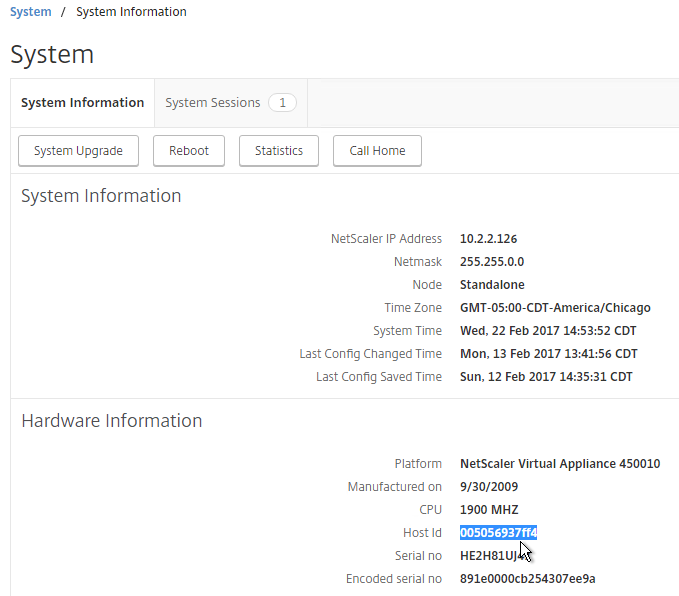
- In the right pane, look down for the Host Id field. This is the MAC address you need for license allocation.
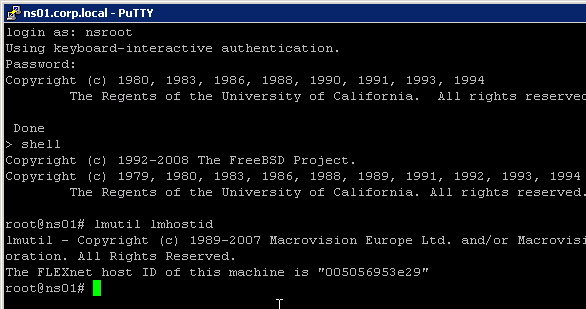
- Another option is to SSH to the appliance and run
shell. - Then run
lmutil lmhostid. The MAC address is returned.
Licensing – Citrix.com
- Login to http://mycitrix.com.
- On the left, click All Licensing Tools.
- On the right, in the top right horizontal menu, click Activate and Allocate Licenses.
- If you are activating an eval license, click Don’t see your product near the top, and enter the eval license key.
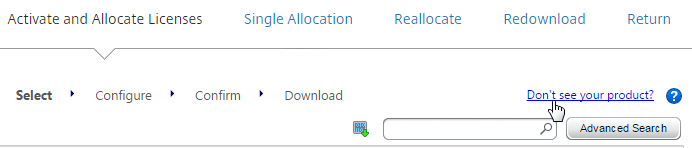
- Otherwise, check the box next to a Citrix NetScaler VPX or MPX license, and click Continue.
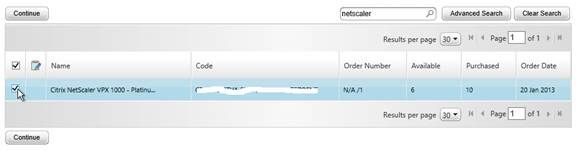
- If this is a NetScaler MPX license then there is no need to enter a host ID for this license. so just click Continue.
- If this is a NetScaler VPX license, enter the VPX MAC address into the Host ID field. It’s not obvious, but you can enter text in this drop-down field.
- If you have more than one VPX license, change the Quantity field to 1, and then click Continue.
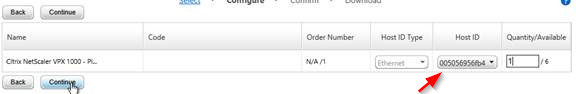 For a VPX appliance, you can get the Host ID by looking at the System Information page. Click the System node to see this page.
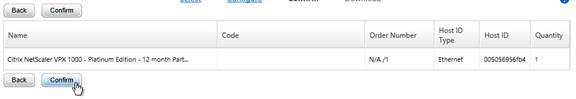
For a VPX appliance, you can get the Host ID by looking at the System Information page. Click the System node to see this page.
- Click Confirm.
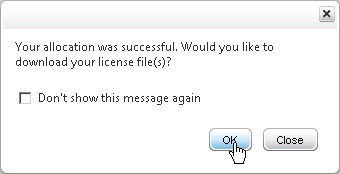
- Click OK when asked to download the license file.
- Click Download.
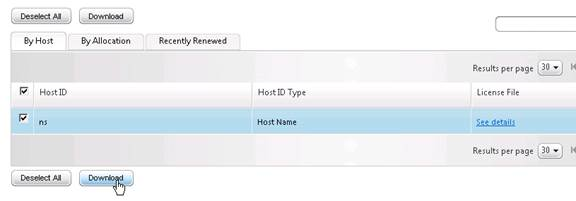
- Click Save and put it somewhere where you can get to it later.
- If you are running NetScaler 11.1 build 51 or newer, then 500 or more NetScaler Gateway Universal Licenses are already included in your NetScaler platform license. NetScaler Standard comes with 500 Gateway Universal, NetScaler Enterprise comes with 1,000 Gateway Universal, and NetScaler Platinum comes with unlimited Gateway Universal.
- If you need more Gateway Universal licenses on your NetScaler, you can allocate them now. These licenses can come from XenMobile Enterprise, XenApp/XenDesktop Platinum Edition, NetScaler Platinum Edition, or a la carte.

- Enter your appliance hostname as the Host ID for all licenses. If you have two appliances in a HA pair, allocate these licenses to the first appliance hostname, then reallocate them to the second appliance hostname.

- Click Confirm.
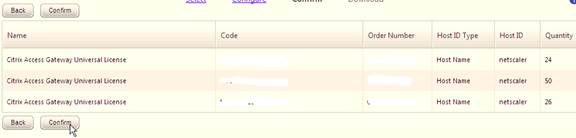
- Click OK when prompted to download your license file.

- Click Download.
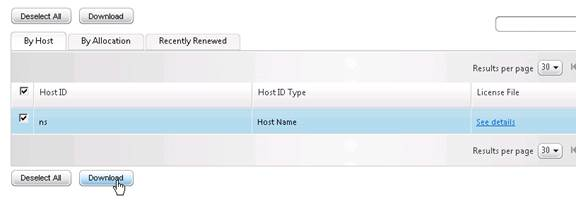
- Click Save.
- If you have two appliances in a High Availability pair with different hostnames then you will need to return the NetScaler Gateway Universal licenses and reallocate them to the other hostname. The top right horizontal menu bar has a Reallocate option.

Install Licenses on Appliance
If you haven’t already installed licenses on your appliance, then do the following:
- In the NetScaler Configuration GUI, on the left, expand System and click Licenses.
- On the top right, click Manage Licenses.
- Click Add New License.
- If you have a license file, select Upload license files from a local computer and then click Browse. Select the license file and click Open.
 License files are stored in
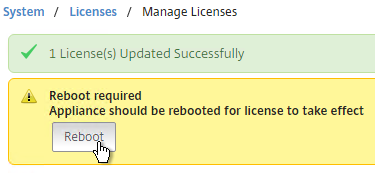
License files are stored in/nsconfig/license. - Click Reboot when prompted. Login after the reboot.
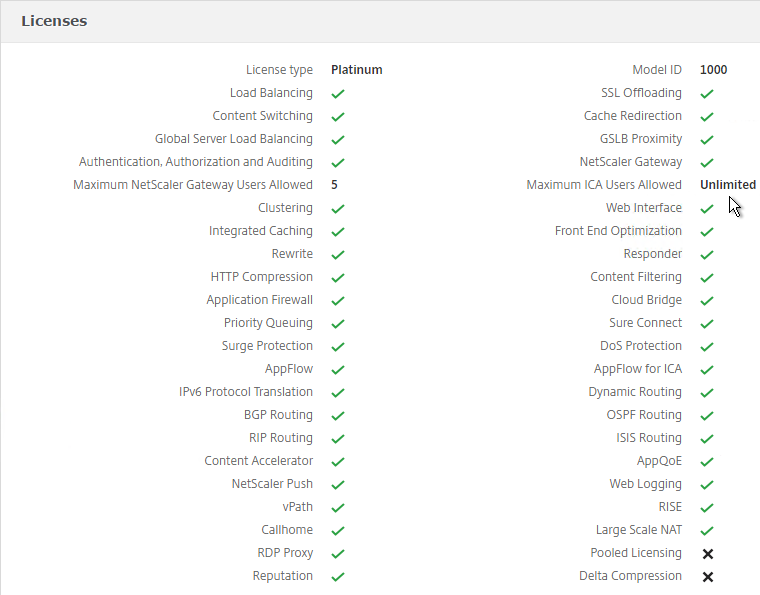
- After rebooting, the Licenses node should look something like this. Notice that Maximum ICA Users Allowed is set to Unlimited.
- Maximum NetScaler Gateway Users Allowed will vary depending on your NetScaler Edition.
- Note: the NetScaler SNMP counter allnic_tot_rx_mbits must remain less than the licensed bandwidth or packets will drop.
Upgrade Firmware
Citrix CTX220371 Must Read Articles Before and After Upgrading NetScaler
Citrix CTX127455 How to Upgrade Software of the NetScaler Appliances in a High Availability Setup
- Download firmware. Ask your Citrix Partner or Citrix Support TRM for recommended versions and builds. At the very least, watch the Security Bulletins to determine which versions and builds resolve security issues. You can also subscribe to the Security Bulletins at http://support.citrix.com by clicking the Alerts (bell) link on the top right after logging in.

- Make sure you Save the config before beginning the upgrade.

- Transferring the firmware upgrade file to the appliance will be slow unless you license the appliance first. An unlicensed appliance will reduce the maximum speed to 1 Mbps.
- When upgrading from 10.5 or older, make sure the NetScaler Gateway Theme is set to Default or Green Bubbles. After the upgrade, you’ll have to create a new Portal Theme and bind it to the Gateway vServers.
- Start with the Secondary appliance.
- Before upgrading the appliance, consider using WinSCP or similar to back up the /flash/nsconfig directory.
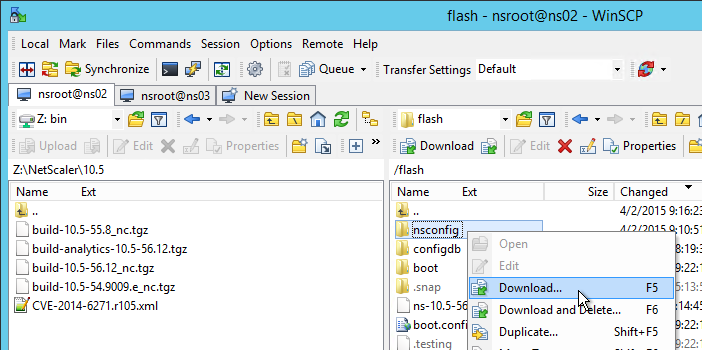
- In the NetScaler GUI, with the top left node (System) selected, on the right, click System Upgrade.
- Click Choose File and browse to the build…tgz file. If you haven’t downloaded firmware yet then you can click the Download Firmware link.
- Click Upgrade.
- The firmware will upload.
- You should eventually see a System Upgrade window with text in it. Click Yes when prompted to reboot.
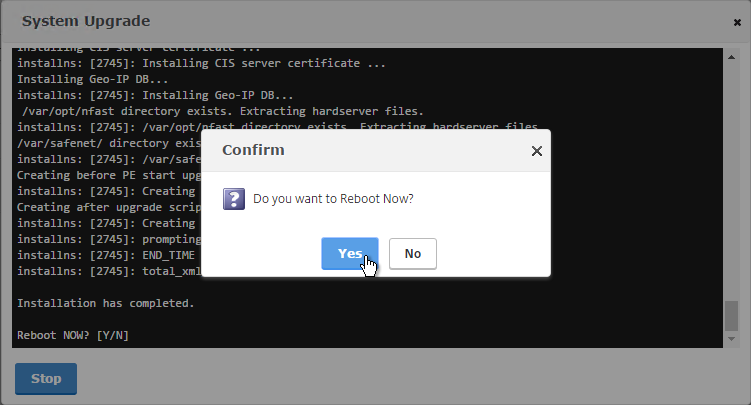
- Once the Secondary is done, login and failover the pair.
- Then upgrade the firmware on the former Primary.
To install firmware by using the command-line interface
- To upload the software to the NetScaler Gateway, use a secure FTP client (e.g. WinSCP) to connect to the appliance.
- Create a version directory under
/var/nsinstall(e.g. /var/nsinstall/11.1.47). - Copy the software from your computer to the
/var/nsinstall/<version>(e.g. /var/nsinstall/11.1.47) directory on the appliance. - Open a Secure Shell (SSH) client (e.g. Putty) to open an SSH connection to the appliance.
- At a command prompt, type
shell. - At a command prompt, type
cd /var/nsinstall/<version>to change to the nsinstall directory. - To view the contents of the directory, type
ls. - To unpack the software, type
tar -xvzf build_X_XX.tgz, wherebuild_X_XX.tgzis the name of the build to which you want to upgrade. - To start the installation, at a command prompt, type
./installns. - When the installation is complete, restart NetScaler.
- When the NetScaler restarts, at a command prompt type
whatorshow versionto verify successful installation.
High Availability
Configure High Availability as soon as possible so almost all configurations are synchronized across the two appliances. The Synchronization exceptions are mainly network interface configurations.
High Availability will also sync files between the two appliances. See CTX138748 File Synchronization in NetScaler High Availability Setup for more information.
- Prepare the secondary appliance:
- Configure a NSIP.
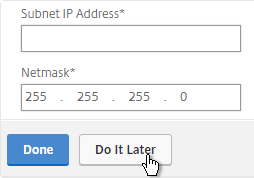
- Don’t configure a SNIP. In Step 2, Subnet IP Address, you can click Do It Later to skip the wizard. You’ll get the SNIP later when you pair it.
- Configure Hostname and Time Zone. Don’t configure DNS since you’ll get those addresses when you pair it.
- License the secondary appliance.
- Upgrade firmware on the secondary appliance. The firmware of both nodes must be identical.
- On the secondary appliance, go to System > High Availability, double-click the local node, and change High Availability Status to STAY SECONDARY. If you don’t do this then you run the risk of losing your config when you pair the appliances. See Terence Luk Creating a Citrix NetScaler High Availability pair without wiping out an existing configuration for more information.
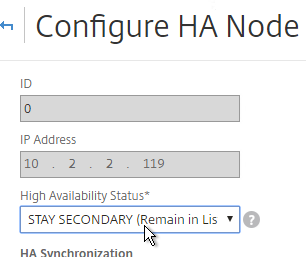
set ha node -hastatus STAYSECONDARY
- On the primary appliance, on the left, expand System, expand Network and click Interfaces.
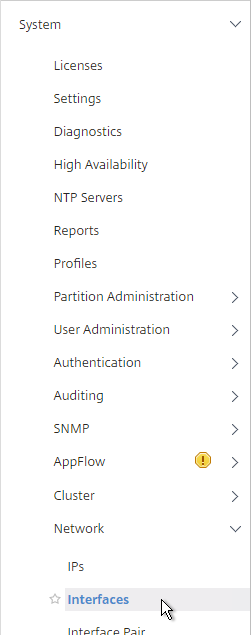
- On the right, look for any interface that is currently DOWN.
- You need to disable those disconnected interfaces before enabling High Availability. Right-click the disconnected interface, and click Disable. Repeat for the remaining disconnected interfaces.
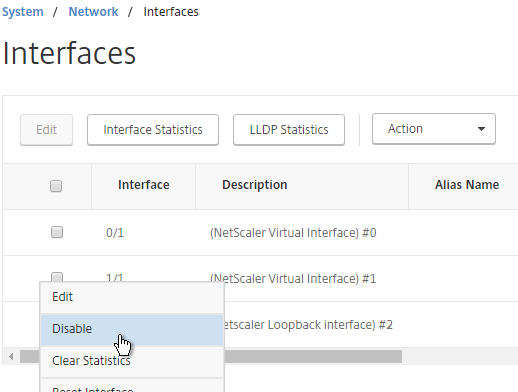
show interface disable interface 1/1
- On the left, expand System and click High Availability.
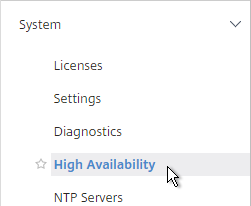
- On the right, double-click node 0 to edit it.

- Change the High Availability Status to STAY PRIMARY, and click OK.

- On the right, click Add.
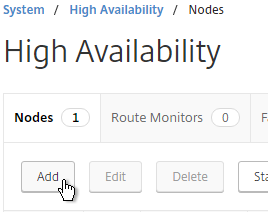
- Enter the other NetScaler’s IP address.
- Enter the other NetScaler’s login credentials, and click Create.
add ha node 1 192.168.123.14Note: this CLI command must be run separately on each appliance. - If you click the refresh icon near the top right, Synchronization State will probably say IN PROGRESS.
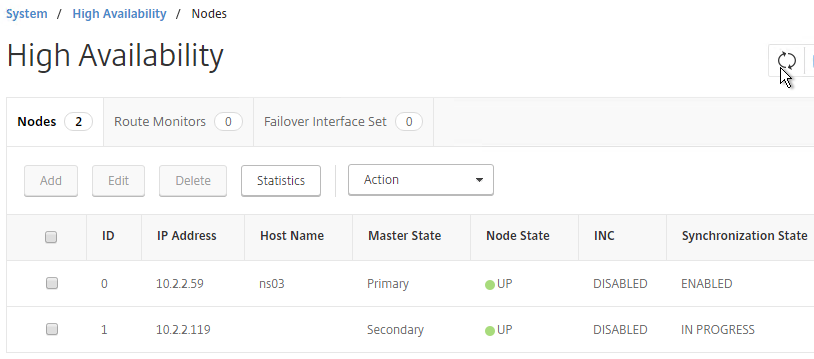
- Eventually it will say SUCCESS.
- To enable Fail-safe mode, edit Node ID 0 (the local appliance).
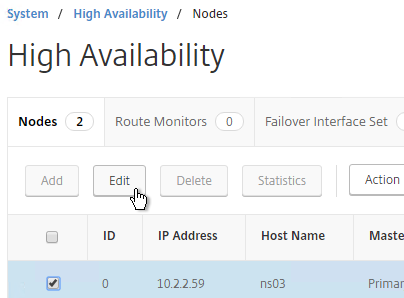
- Change High Availability State back to ENABLED.

- Under Fail-safe Mode, check the box next to Maintain one primary node even when both nodes are unhealthy. Scroll down, and click OK.
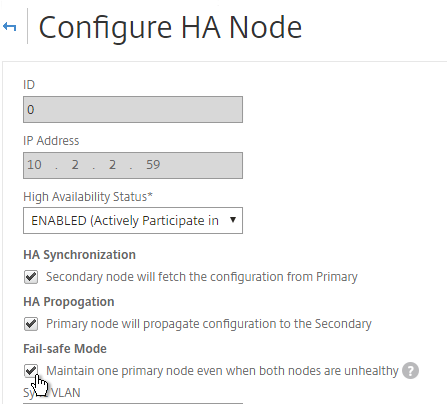
set ha node -failSafe ON
- Change High Availability State back to ENABLED.
- If you login to the Secondary appliance, you might see a message warning you against making changes. Always apply changes to the Primary appliance.
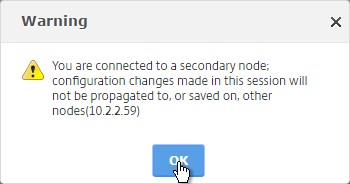
- On the secondary appliance, go to System > High Availability, edit the local node, and change it from STAY SECONDARY to ENABLED.
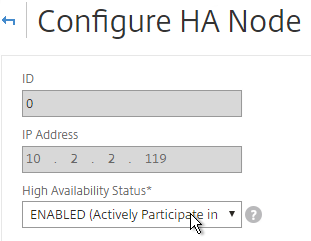
- Go to System > Network > Routes, and make sure you don’t have two 0.0.0.0 routes. Joining an appliance to an HA pair causes the default route on the primary appliance to sync to the secondary appliance. But, it doesn’t delete the default gateway that was formerly configured on the secondary appliance.

- From the NetScaler CLI (SSH), run “sh ha node” to see the status. You should see heartbeats on all interfaces. If not, configure VLANs as detailed in the next section.
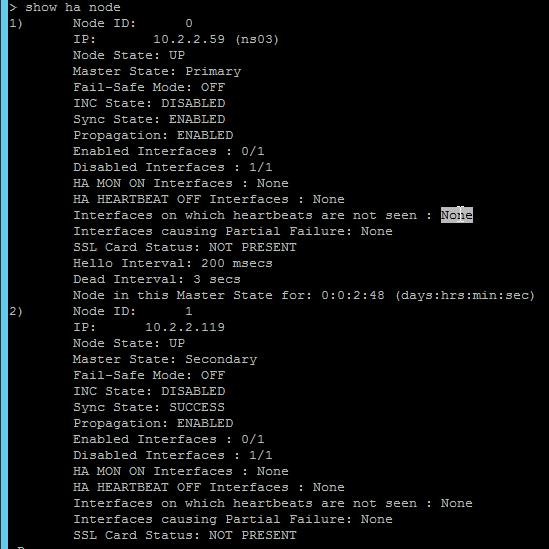
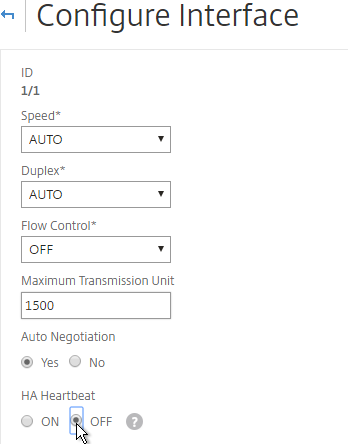
- You can also disable HA heartbeats on specific interfaces.
- Note: Make sure HA heartbeats are enabled on at least one interface/channel.
- Note: this is an interface configuration, so this configuration change is not propagated to the other node.
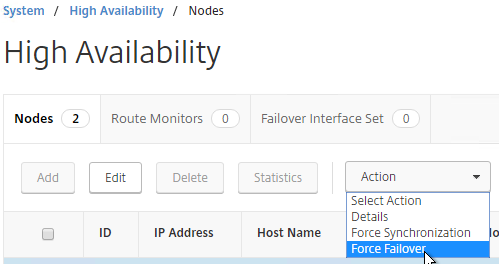
- You can force failover of the primary appliance by going to System > High Availability, opening the Actions menu, and clicking Force Failover.
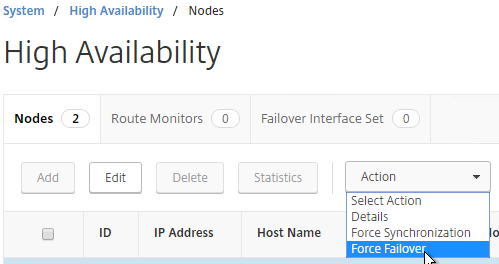
force ha failoverIf your firewall (e.g. Cisco ASA) doesn’t like Gratuitous ARP, see CTX112701 – The Firewall Does not Update the Address Resolution Protocol Table
Port Channels on Physical NetScaler MPX
If you are configuring a NetScaler MPX (physical appliance), and if you plugged in multiple cables, and if more than one of those cables is configured on the switch for the same VLAN(s), then you must bond the interfaces together by configuring a Port Channel. On the switch, create a Port Channel, preferably with LACP enabled. The Port Channel can be an Access Port (one VLAN), or a Trunk Port (multiple VLANs). On the NetScaler, configure LACP on the network interfaces, or create a Channel manually. Both are detailed below.
Also see Webinar: Troubleshooting Common Network Related Issues with NetScaler.
LACP Port Channel
To configure Port Channels on a NetScaler, you can either enable LACP, or you can configure a Channel manually. If your switch is configured for LACP, do the following on NetScaler to enable LACP on the member interfaces.
- Go to System > Network > Interfaces.
- On the right, edit one of the Port Channel member interfaces.
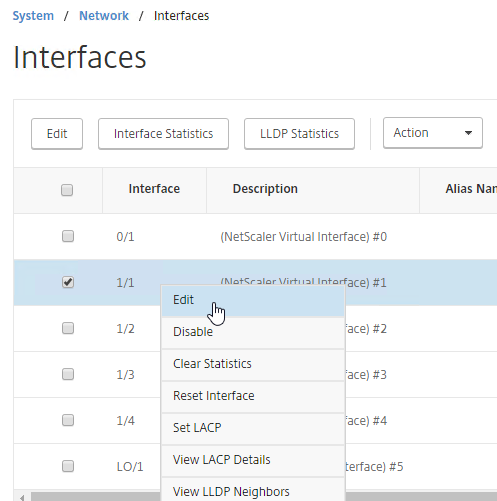
- Scroll down.
- Check the box next to Enable LACP.
- In the LACP Key field, enter a number. The number you enter here becomes the channel number. For example, if you enter 1, NetScaler creates a Channel named LA/1. All member interfaces of the same Port Channel must have the same LACP Key. Click OK when done.
- Continue enabling LACP on member interfaces and specifying the key (channel number). If you are connected to two port channels, one set of member interfaces should have LACP Key 1, while the other set of member interfaces should have LACP Key 2.
- Note: in an HA pair, you must perform this interface configuration on both nodes. The LACP commands are not propagated across the HA pair.
- If you go to System > Network > Channels.
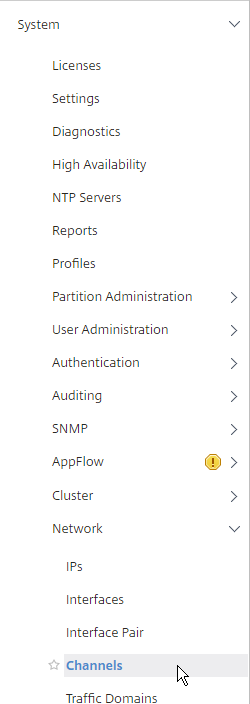
- You’ll see the LACP Channels on the right. These were created automatically.
- If you edit a Channel, there’s a LACP Details tab that shows you the member interfaces.
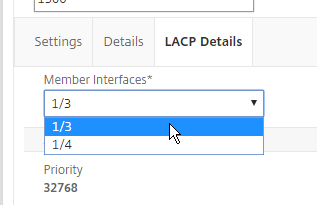
Manual Channel
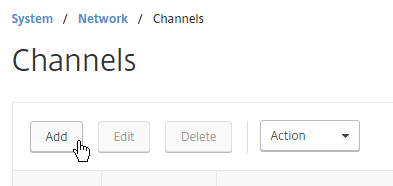
If your switch is not configured for LACP, then you can instead create a Channel manually.
- Go to System > Network > Channels.
- On the right, click Add.
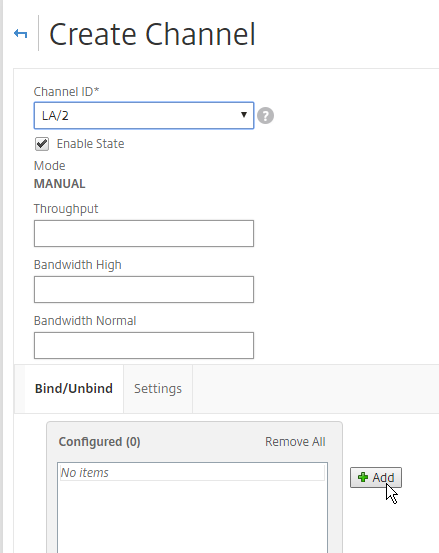
- At the top, choose an unused Channel ID (e.g. LA/2).
- On the bottom, click Add.
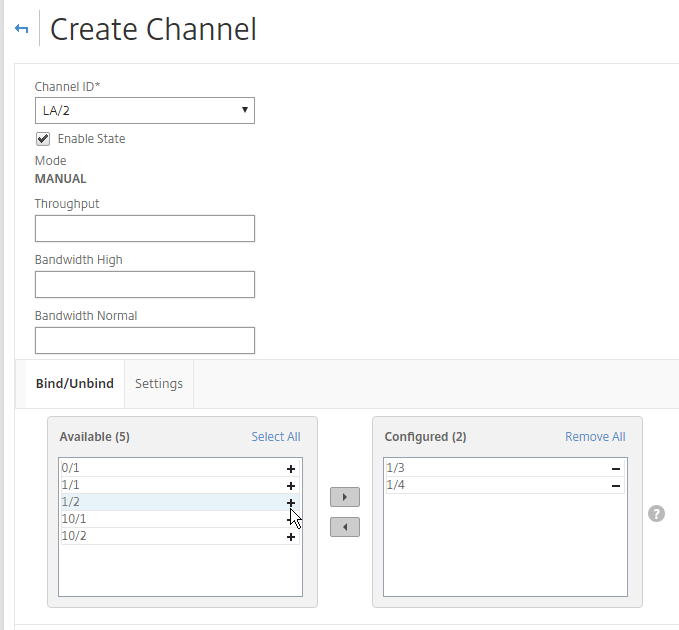
- Click the plus icon next to each member interface to move it to the right. Then click Create.
Redundant Interface Set
You can also configure the NetScaler for switch-independent teaming. Create a Channel manually, but select a Channel ID starts with LR instead of LA. This is called Link Redundancy or Redundant Interface Set.
Channel Minimum Throughput
Channels can be configured so that a High Availability failover occurs when the Channel throughput drops below a configured value. For example, if you have four members in a Channel, you might want a High Availability failover to occur when two of the member interfaces fail.
- Go to System > Network > Channels, and edit a Channel.
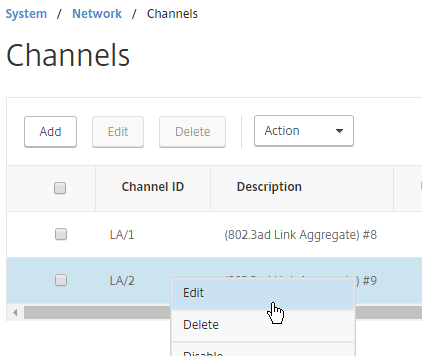
- Near the top, enter a minimum threshold value in the Throughput field. If the total bonded throughput drops below this level, a High Availability failover will occur.
Trunk Port and High Availability
If you are trunking multiple VLANs across the channel, and if every VLAN is tagged (no native VLAN), then a special configuration is needed to allow High Availability heartbeats across the channel.
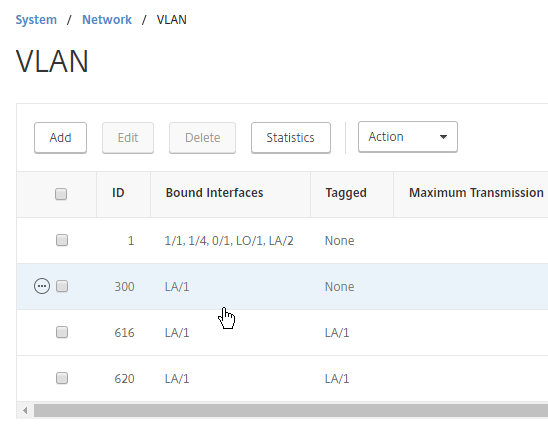
- Go to System > Network > VLAN.
- Add VLAN objects, and bind to the channel (e.g. LA/1).
- To bind multiple VLANs to a single interface/channel, the VLANs must be tagged.
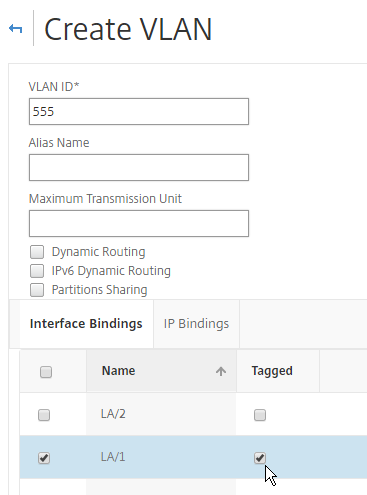
- Configure one of the VLANs as untagged. Only untag one of them. Which one you untag doesn’t matter, except that the same VLAN should be untagged on the other HA node. If your switch doesn’t allow untagged packets, don’t worry, we’ll fix that soon.
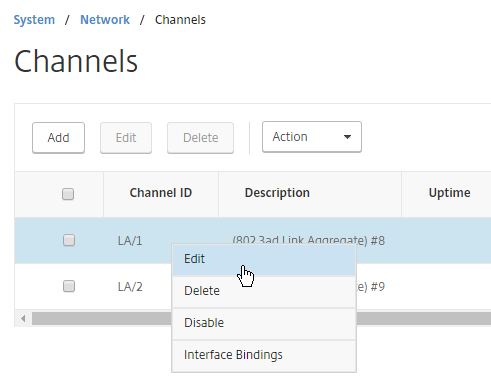
- If your switch doesn’t allow untagged packets, go to System > Network > Channels, and edit the channel.
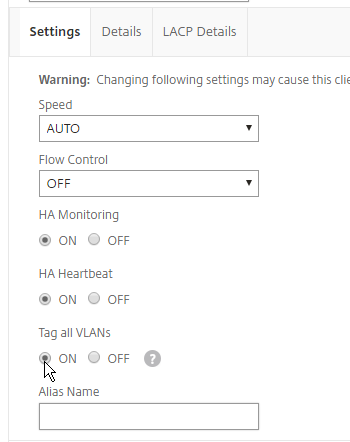
- Scroll down. On the Settings tab, set Tag all VLANs to ON. This causes NetScaler to tag all packets, including the VLAN you formerly marked as untagged. This special configuration is necessary to also tag High Availability heartbeat packets.
- Note: in an HA pair, you must perform this Tagall configuration on both nodes. The Tagall command is not propagated across the HA pair.
Common physical interface configuration
Here is a common NetScaler networking configuration for a physical NetScaler MPX that is connected to both internal and DMZ.
Note: If the appliance is connected to both DMZ and internal, then be aware that this configuration essentially bypasses (straddles) the DMZ-to-internal firewall. That’s because if a user connects to a public/DMZ VIP, then NetScaler could use an internal SNIP to connect to the internal server: in other words, traffic comes into a DMZ VLAN, but goes out an internal VLAN. A more secure approach is to have different appliances for internal and DMZ. Or use NetScaler SDX, partitioning, or traffic domains.
- 0/1 connected to a dedicated management network. NSIP is on this network.
- 0/1 is not optimized for high throughput so don’t put data traffic on this interface. If you don’t have a dedicated management network, then put your NSIP on one of the other interfaces (1/1, 10/1, LA/1, etc.) and don’t connect any cables to 0/1.
- To prevent NetScaler from using this dedicated management interface for outbound data traffic, don’t put a SNIP on this management network, and configure the default gateway (route 0.0.0.0) to use a router on a different data network (typically the DMZ VLAN). However, if there’s no SNIP on this VLAN, and if the default gateway is on a different network, then there will be asymmetric routing for management traffic, since inbound management traffic goes in 0/1, but reply traffic goes out LA/1 or LA/2. To work around this problem, enable Mac Based Forwarding, or configure Policy Based Routing. Both of these options are detailed in the next section.
- It’s easiest if the switch port for this dedicated management interface is an Access Port (untagged). If VLAN tagging is required, then NSVLAN must be configured on the NetScaler.
- 10/1 and 10/2 in a LACP port channel (LA/1) connected to internal VLAN(s). Static routes to internal networks through a router on one of these internal VLANs.
- If only one internal VLAN, configure the switch ports/channel as an Access Port.
- If multiple internal VLANs, configure the switch ports/channel as a Trunk Port. Set one of the VLANs as the channel’s Native VLAN so it doesn’t have to be tagged.
- If the networking team is unwilling to configure a Native VLAN on the Trunk Port, then NetScaler needs special configuration (tagall) to ensure HA heartbeat packets are tagged.
- 1/1 and 1/2 in a LACP port channel (LA/2) connected to DMZ VLAN(s). The default gateway (route 0.0.0.0) points to a router on a DMZ VLAN so replies can be sent to Internet clients.
- If only one DMZ VLAN, configure the switch ports/channel as an Access Port.
- If multiple DMZ VLANs, configure the switch ports/channel as a Trunk Port. Set one of the VLANs as the channel’s Native VLAN so it doesn’t have to be tagged.
- If the networking team is unwilling to configure a Native VLAN on the Trunk Port, then NetScaler needs special configuration (tagall) to ensure HA heartbeat packets are tagged.
Dedicated Management Subnet
Dedicated Management Subnet implies that your NetScaler is connected to multiple VLANs. If you have a subnet that is for NSIP only, and don’t want to use the NSIP subnet for data traffic, then you’ll want to move the default route to a different subnet, which breaks the NSIP. To work around this problem, create a PBR for the NSIP to handle replies from NSIP, and to handle traffic sourced by the NSIP.
- Go to System > Network > PBRs.

- On the right, click Add.

- Give the PBR a name (e.g. NSIP)
- Set the Next Hop Type drop-down to New.
- In the Next Hop field, enter the router IP address that is on the same network as the NSIP.

- In the Configure IP section, set the first Operation drop-down to =.
- In the Source IP Low field, enter the NSIP. This causes the PBR to match all traffic with NSIP as the Source IP address.
- You don’t need anything else.

- Scroll down, and click Create.

- To handle DNS traffic sourced by the NSIP, create another PBR by right-clicking the existing one, and clicking Add.

- Change the name to NSIP-DNS or similar.
- Change the Action drop-down to DENY. This prevents the PBR from overriding normal DNS behavior.
- Change the Priority to a lower number than the original PBR. Scroll down.

- In the Configure Protocol section, click the Protocol drop-down, and select UDP (17).

- In the Destination section, change the Operation to =.
- In the Destination port Low field, enter 53.

- Scroll down, and click Create.

- Make sure the DENY PBR is higher in the list (lower priority number) than the ALLOW PBR.

- Then open the Action menu, and click Apply.

add ns pbr NSIP-DNS DENY -srcIP = 10.2.2.126 -destPort = 53 -nextHop 10.2.2.1 -protocol UDP -priority 5 add ns pbr NSIP ALLOW -srcIP = 10.2.2.59 -nextHop 10.2.2.1 apply ns pbrs
If you want a floating management IP that is always on the Primary appliance, here’s a method of granting management access without adding a SNIP to the management subnet:
- Create a Load Balancing Service on HTTP 80 on IP address 127.0.0.1. You might already have one called AlwaysUp that is used with SSL Redirects. Note: NetScaler doesn’t allow creating a Load Balancing service on IP address 127.0.0.1 and port 443 (SSL).
- The IP address you enter is 127.0.0.1. When you view the Load Balancing Service, it shows the local NSIP. After a HA failover, the IP Address will change to the other NSIP.

- The IP address you enter is 127.0.0.1. When you view the Load Balancing Service, it shows the local NSIP. After a HA failover, the IP Address will change to the other NSIP.
- Create a Load Balancing Virtual Server using a VIP on the management subnet. Protocol = SSL. Port number = 443.

- Bind the AlwaysUp:80 or loopback:80 service to the Load Balancing Virtual Server. In summary: the front end is 443 SSL, while the LB Service is 80 HTTP.

- Bind the AlwaysUp:80 or loopback:80 service to the Load Balancing Virtual Server. In summary: the front end is 443 SSL, while the LB Service is 80 HTTP.
- Add the new VIP to the PBRs so the replies go out the correct interface.

- You should then be able to point your browser to https://Step2VIP to manage the appliance.
- You can perform the same loopback trick for 22 SSH. Create a Load Balancing Service on TCP 22 on IP address 127.0.0.1.

- Create a Load Balancing Virtual Server using the management VIP specified earlier. Protocol = TCP. Port number = 22.

- Bind the loopback:TCP:22 service to the Load Balancing Virtual Server.

- Bind the loopback:TCP:22 service to the Load Balancing Virtual Server.
- You should then be able to point your SSH Client to <Step2VIP> to manage the appliance.
- CLI Commands for the floating management VIP:
add service AlwaysUp 127.0.0.1 HTTP 80 add service mgmt-SSH 127.0.0.1 TCP 22 add lb vserver mgmt-SSL SSL 10.2.2.128 443 add lb vserver mgmt-SSH TCP 10.2.2.128 22 bind lb vserver mgmt-SSL AlwaysUp bind lb vserver mgmt-SSH mgmt-SSH set ns pbr NSIP-DNS DENY -srcIP = 10.2.2.126-10.2.2.128 -destPort = 53 -nextHop 10.2.2.1 -protocol UDP -priority 5 set ns pbr NSIP ALLOW -srcIP = 10.2.2.126-10.2.2.128 -nextHop 10.2.2.1 apply ns pbrs
Multiple Subnets / Multiple VLANs
Citrix CTX214033 Networking and VLAN Best Practices for NetScaler discusses many of the same topics detailed in this section.
If this is a physical MPX appliance, see the previous Port Channel section first.
If you only connected NetScaler to one subnet (one VLAN) then skip ahead to DNS servers.
Configuration Overview
The general configuration process for multiple subnets is this:
- Create a SNIP for each subnet/VLAN.
- Create a VLAN object for each subnet/VLAN.
- Bind the VLAN object to the SNIP for the subnet.
- Bind the VLAN object to the Port Channel or single interface that is configured for the VLAN/subnet.
SNIPs for each VLAN
You will need one SNIP for each connected subnet/VLAN. VLAN objects (tagged or untagged) bind the SNIPs to particular interfaces. NetScaler uses the SNIP’s subnet mask to assign IP addresses to particular interfaces.
NSIP Subnet
The NSIP subnet is special so you won’t be able to bind it to a VLAN. Use the following SNIP/VLAN method for any network that does not have the NSIP. The remaining interfaces will be in VLAN 1, which is the VLAN that the NSIP is in. VLAN 1 is only locally significant so it doesn’t matter if the switch is configured with it or not. Just make sure the switch has a native VLAN configured, or configure the interface as an access port. If you require trunking of every VLAN, including the NSIP VLAN, then additional configuration is required (NSVLAN or Tagall).
Configure Subnets/VLANs
To configure NetScaler with multiple connected subnets:
- Add a subnet IP for every network the NetScaler is connected to, except the dedicated management network. Expand System, expand Network, and click IPs.
- On the right, click Add.
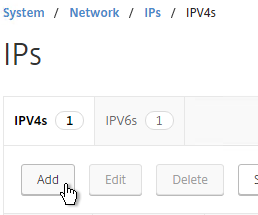
- Enter the Subnet IP Address for this network/subnet. This SNIP will be the source IP address the NetScaler will use when communicating with any other service/server on this network. The Subnet IP is also known as the Interface IP for the network. You will need a separate SNIP for each connected network (VLAN).
- Enter the netmask for this network.
- Ensure the IP Type is set to Subnet IP. Scroll down.
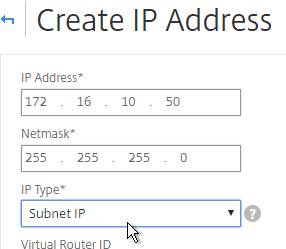
add ns ip 172.16.1.11 255.255.255.0 -type SNIP
- Under Application Access Controls, decide if you want to enable GUI management on this SNIP. This is particularly useful for High Availability pairs, because when you point your browser to the SNIP, only the primary appliance will respond. However, enabling management access on the SNIP can be a security risk, especially if this is a SNIP for a DMZ network.
- Click Create when done.
- Continue adding SNIPs for each connected network (VLAN).
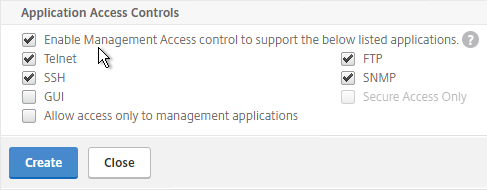
set ns ip 172.16.1.11 -mgmtAccess ENABLED -telnet DISABLED -ftp DISABLED
- On the left, expand System, expand Network, and click VLANs.
- On the right, click Add.
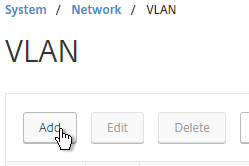
- Enter a descriptive VLAN ID. The actual VLAN ID only matters if you intend to tag the traffic. If not tagged, then any ID (except 1) will work.
- Check the box next to one physical interface or channel (e.g. LA/1) that is connected to the network.
- If this is a trunk port, select Tagged if the switch port/channel is expecting the VLAN to be tagged.
- If your switches do not allow untagged packets, then you will need to use the tagall interface option to tag NetScaler High Availability heartbeat packets. See CTX122921 – Citrix NetScaler Interface Tagging and Flow of High Availability Packets
- If you don’t tag the VLAN, then the NetScaler interface/channel is removed from VLAN 1, and instead put in this VLAN ID.
- Switch to the IP Bindings tab.
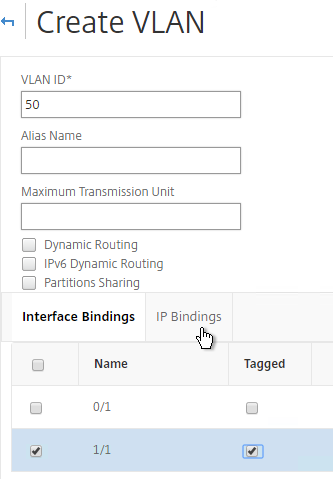
- Check the box next to the Subnet IP for this network. This lets NetScaler know which interface is used for which IP subnet. Click Create when done.
add vlan 50 bind vlan 50 -ifnum LA/1 -IPAddress 172.16.1.11 255.255.255.0
- On the left, expand System, expand Network, and click Routes.
- On the right, click Add.
- Internal networks are usually only accessible through an internal router. Add a static routes to the internal networks, and set the Gateway (next hop) to an internal router.
- Make sure NULL Route is set to No.
- Set the Gateway (Next Hop) to an internal router.
- Then click Create.
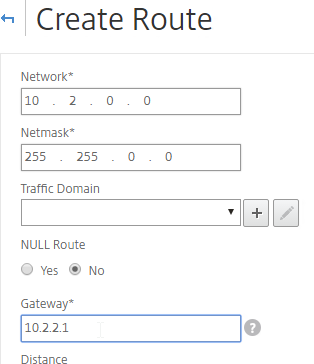
add route 10.2.0.0 255.255.0.0 10.2.2.1
- The default route should be changed to use a router on the DMZ network (towards the Internet). Before deleting the existing default route, either enable Mac Based Forwarding, or create a Policy Based Route, so that the replies from NSIP can reach your machine. You usually only need to do this for dedicated management networks.
- Note: PBR is recommended over MBF, because PBR can handle traffic sourced by NSIP (e.g Syslog traffic), while MBF cannot.
- Mac Based Forwarding sends replies out the same interface they came in on. However, MBF ignores the routing table, and doesn’t handle traffic sourced by the NSIP (e.g. LDAP traffic). To enable MBF:
- On the left, expand System, and click Settings.

- On the right, in the left column, click Configure modes.

- Check the box next to MAC Based Forwarding (MBF), and click OK. More info on MAC Based Forwarding can be found at Citrix CTX1329532 FAQ: Citrix NetScaler MAC Based Forwarding (MBF).

- On the left, expand System, and click Settings.
- Go back to System > Network > Routes. On the right, delete the 0.0.0.0 route. Don’t do this unless the NetScaler has a route, PBR, or MBF to the IP address of the machine you are running the browser on.
rm route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.2.2.1 - Then click Add.
- Set the Network to 0.0.0.0, and the Netmask to 0.0.0.0.
- Make sure NULL Route is set to No.
- Enter the IP address of the DMZ (or data) router, and click Create.
add route 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 172.16.1.1
DNS Servers
- To configure DNS servers, expand Traffic Management, expand DNS, and click Name Servers.
- On the right, click Add.
- Enter the IP address of a DNS server, and click Create.
- Note: The NetScaler must be able ping each of the DNS servers or they will not be marked as UP. The ping originates from the SNIP.
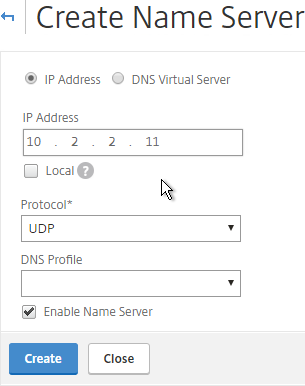
add dns nameServer 10.2.2.11 - NetScaler 11.1 build 51 and newer includes DNS Security Options, which are useful if you use this NetScaler to provide DNS services to clients (e.g. DNS Proxy/Load Balancing, GSLB, etc.).
NTP Servers
- On the left, expand System, and click NTP Servers.
- On the right, click Add.
- Enter the IP Address of your NTP Server (or pool.ntp.org) and click Create.
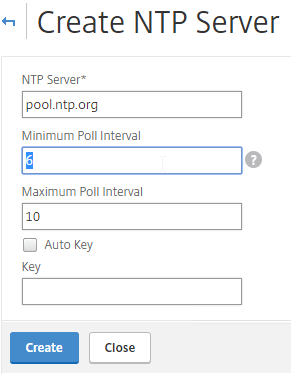
add ntp server pool.ntp.org - Open the Action menu and click NTP Synchronization.
- Select ENABLED and click OK.
enable ntp sync - You can click the System node to view the System Time.
- If you need to manually set the time, SSH (Putty) to the NetScaler appliances. Run date to set the time. Run date –help to see the syntax.
- Ntpdate –u pool.ntp.org will cause an immediate NTP time update.
SYSLOG Server
Citrix CTX120609 NetScaler Log Rotation and Configuration Using Newsyslog
The NetScaler will by default store a few syslogs on the local appliance. You can create a syslog policy to also send the syslog entries to an external server, like Citrix Command Center.
- On the left, expand System, expand Auditing, and click Syslog.
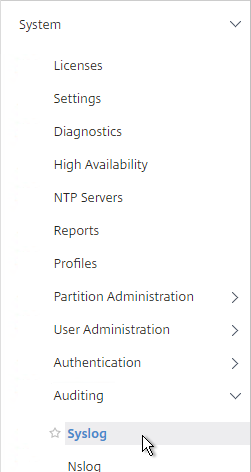
- On the right, switch to the Servers tab and click Add.
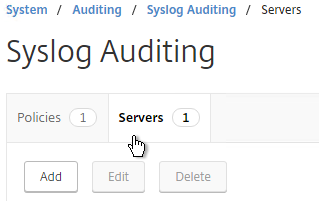
- Enter a name for the Syslog server.
- If 11.1-49 or newer, you can change Server Type to Server Domain Name and enter a FQDN.
- Enter the IP Address or FQDN of the SYSLOG server, and 514 as the port.
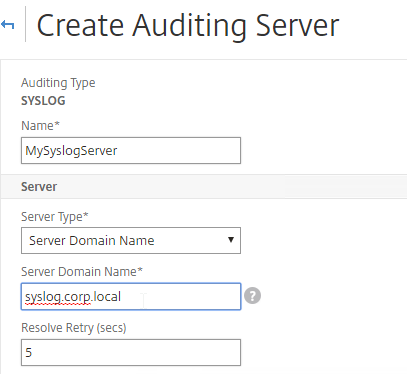
- Configure the Log Levels you’d like to send to it.
- Check the box for TCP Logging if you want the client IP. Note: TCP Logging requires significant disk space on the Syslog server.
- Select your desired Time Zone and then click Create.
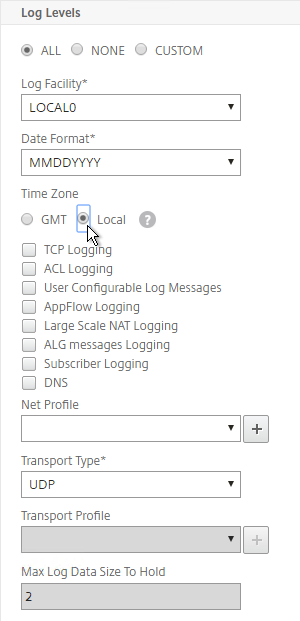
add audit syslogAction MySyslogServer 10.2.2.12 -logLevel ALL -timeZone LOCAL_TIME add audit syslogAction MySyslogServer syslog.corp.local -logLevel ALL -timeZone LOCAL_TIME
- On the right, switch to the Policies tab, and then click Add.
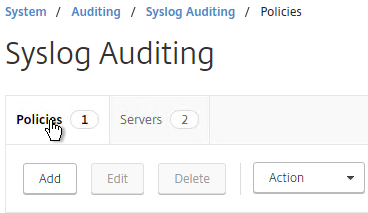
- Give the policy a descriptive name, select the Syslog server, and then click Create.
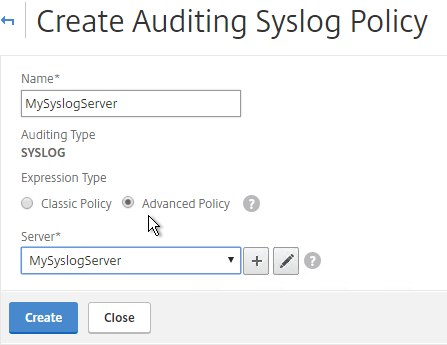
add audit syslogPolicy MySyslogServer ns_true MySyslogServer
- While still on the Policies tab, open the Actions menu, and click Classic Policy Global Bindings or Advanced Policy Global Bindings, depending on which one you chose when creating the Syslog policy.
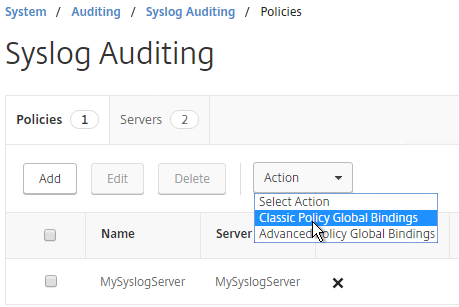
- Click the arrow next to Click to select.
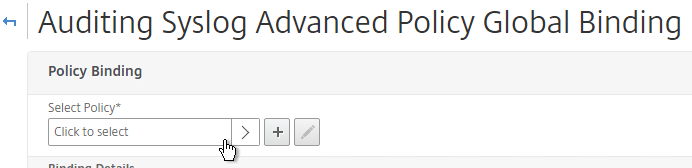
- Select the Syslog policy you want to bind and click Select.
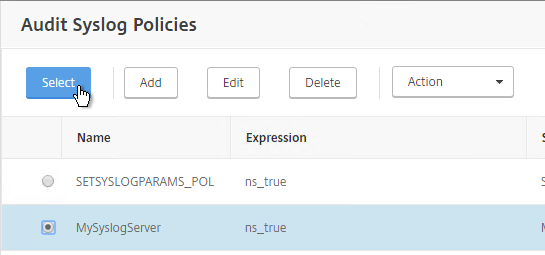
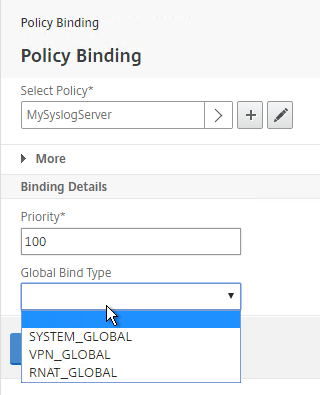
- If you don’t select anything in Global Bind Type, then it defaults to SYSTEM_GLOBAL.
- Click Bind.
- Click Done.
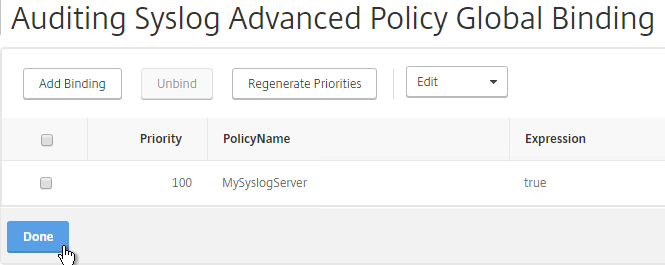
bind audit syslogGlobal -policyName MySyslogServer -priority 100 bind system global MySyslogServer -priority 100
SNMP – MIB, Traps, and Alarms
- On the left, expand System, and click SNMP.
- On the right, click Change SNMP MIB.
- Change the fields as desired. Your SNMP tool (e.g. NetScaler Management and Analytics System) will read this information. Click OK.
- This configuration needs to be repeated on the other node.
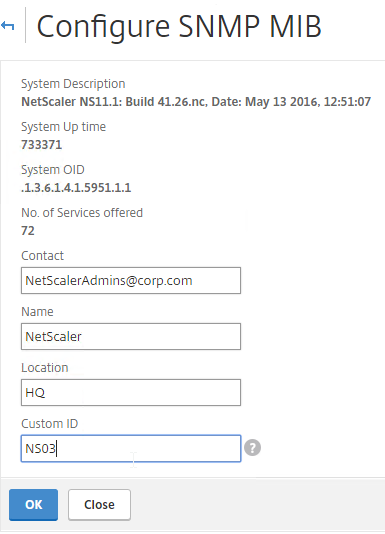
set snmp mib -contact NSAdmins@corp.com -name ns02 -location Corp
- Expand System, expand SNMP, and click Community.
- On the right, click Add.
- Specify a community string and the Permission and click Create.
add snmp community public GET
- On the left, under SNMP, click Traps.
- On the right, click Add.
- Specify a trap destination and Community Name and click Create.
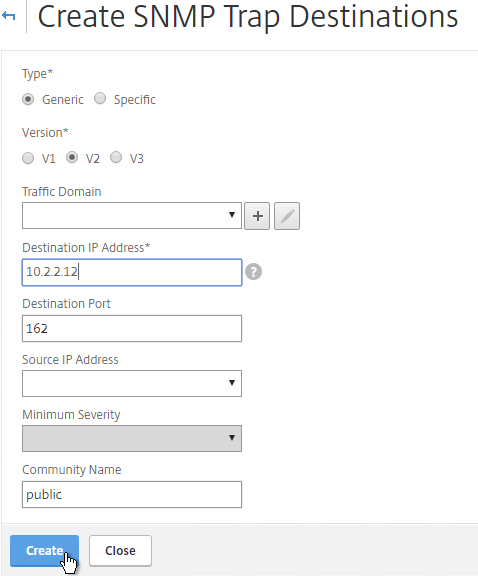
add snmp trap generic 10.2.2.12 -communityName public add snmp trap specific 10.2.2.12 -communityName public
- On the left, under SNMP, click Managers.
- On the right, click Add. Note: if you do not add a manager then the NetScaler will accept SNMP queries from all SNMP Managers on the network.
- Change the selection to Management Network.
- Specify the IP of the Management Host and click Create.
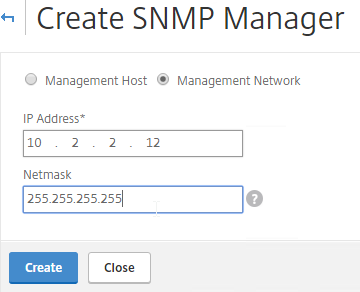
add snmp manager 10.2.2.12
- The Alarms node allows you to enable SNMP Alarms and configure thresholds.
- You can open an alarm to set thresholds. For example, CPU-USAGE can be set to 90% alarm and 50% normal with a Critical severity.
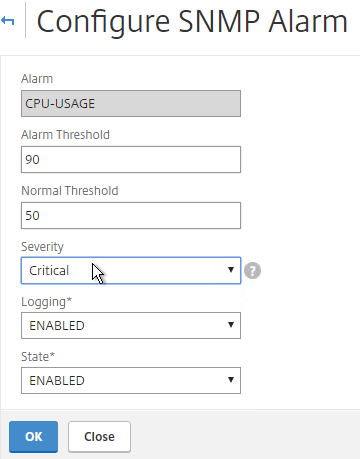
set snmp alarm CPU-USAGE -thresholdValue 90 -normalValue 50 -severity Critical
- You can also configure the MEMORY alarm.
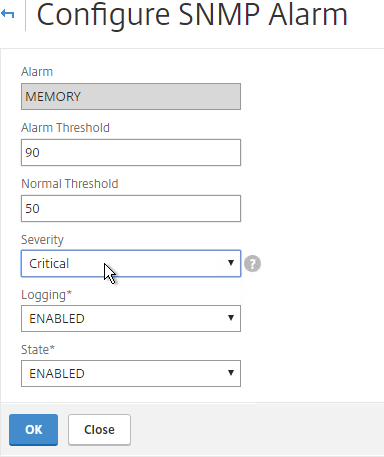
set snmp alarm MEMORY -thresholdValue 90 -normalValue 50 -severity Critical
From http://www.slideshare.net/masonke/net-scaler-tcpperformancetuningintheaolnetwork: In addition to the usual OIDs, we have found these very useful to warn of potential problems.
- ifTotXoffSent – .1.3.6.1.4.1.5951.4.1.1.54.1.43
- ifnicTxStalls – .1.3.6.1.4.1.5951.4.1.1.54.1.45
- ifErrRxNoBuffs – .1.3.6.1.4.1.5951.4.1.1.54.1.30
- ifErrTxNoNSB – .1.3.6.1.4.1.5951.4.1.1.54.1.31
Call Home
Citrix Blog Post – Protect Your NetScaler From Disaster With Call Home!: If you have a physical NetScaler (MPX or SDX) with an active support contract, you many optionally enable Call Home to automatically notify Citrix Technical Support of hardware and software failures.
- On the left, expand System and click Diagnostics.
- On the right, in the left column, in the Technical Support Tools section, click Call Home.
- Check the box next to Enable Call Home.
- Optionally enter an email address to receive notifications from Citrix Technical Support. Click OK.
- If you go back into Call Home, it should indicate if registration succeeded or failed. Successful registration requires an active support contract.
Change nsroot Password
- If you want to force strong passwords for local accounts, go to System > Settings, on the right, click Change Global System Settings
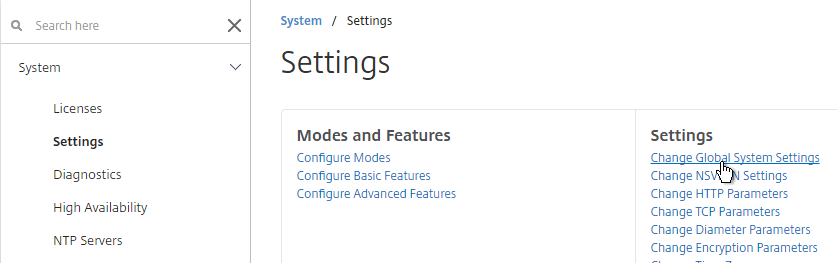
- Scroll down to the Command Line Interface (CLI) section.
- You can change Strong Password to Enable, and also specify a Min Password Length. Click OK.
- Expand System, expand User Administration and click Users.
- On the right, select nsroot, and click Change Password.
- Specify a new password and click OK.
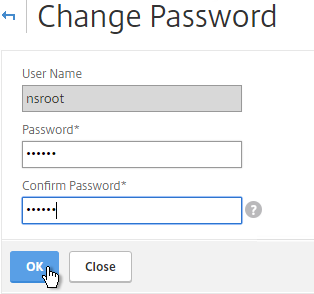
set system user nsroot Passw0rd
TCP, HTTP, SSL, and Security Settings
Citrix Whitepaper Secure Deployment Guide for NetScaler MPX, VPX, and SDX Appliances
Citrix Knowledgebase articles:
- CTX127917 How to Configuring the Rate Limiting Feature of a NetScaler Appliance to Mitigate a DDoS Attack
- CTX131681 How to Use NetScaler Appliance to Avoid Layer 7 DDoS Attacks
- CTX209398 Addressing false positives from CBC and MAC vulnerability scans of SSHD
- On the left, expand System and click Settings.
- On the right side of the right pane, click Change TCP parameters.
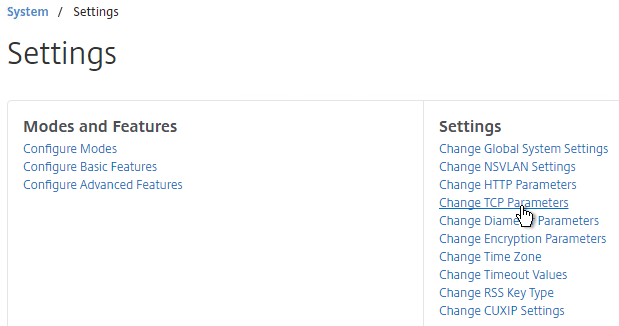
- Check the box for Window scaling (near the top).
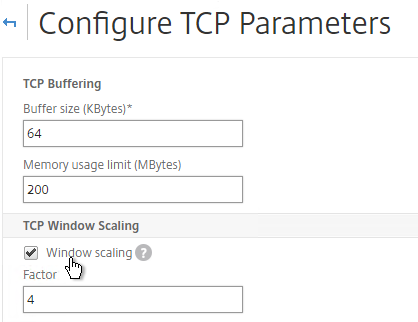
- Scroll down and check the box for Selective Acknowledgement. Click OK.
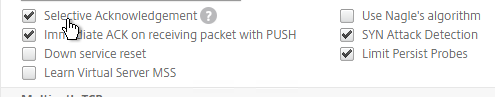
set ns tcpParam -WS ENABLED -SACK ENABLED
- Check the box for Window scaling (near the top).
- On the right, click Change HTTP parameters.

- Under Cookie, change the selection to Version1. This causes NetScaler to set Cookie expiration to a relative time instead of an absolute time.
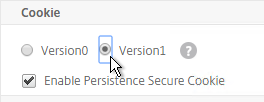
set ns param -cookieversion 1
- Check the box next to Drop invalid HTTP requests.
- Scroll down and click OK.
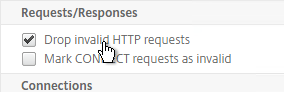
set ns httpParam -dropInvalReqs ON
- Under Cookie, change the selection to Version1. This causes NetScaler to set Cookie expiration to a relative time instead of an absolute time.
- From Citrix CTX232321 Recommended TCP Profile Settings for Full Tunnel VPN/ICAProxy from NetScaler Gateway 11.1 Onwards: 💡
- Expand System, and click Profiles.
- On the right, on the TCP Profiles tab, edit the nstcp_default_profile.

- Enable Window Scaling with a factor of 8.

- Set Minimum RTO (in millisec) = 600.

- Set TCP Buffer Size (bytes) = 600000
- Set TCP Send Buffer Size (bytes) = 600000

- Change TCP Flavor = BIC.

- Enable Use Nagle’s algorithm.

- Click OK when done.
- You can run the following command to see statistics on the dropped packets:
nsconmsg -g http_err_noreuse_ -d stats
- See CTX209398 Addressing false positives from CBC and MAC vulnerability scans of SSHD to harden SSHD by editing /nsconfig/sshd_config with the following. Then run
kill -HUP `cat /var/run/sshd.pid`to restart SSHD.Ciphers aes128-ctr,aes192-ctr,aes256-ctr MACs hmac-sha1,hmac-ripemd160
- Implement Responder policies to prevent Shellshock attack against back-end web servers. See Citrix CTX200277 NetScaler Defends Against Shellshock Attack.
add audit messageaction ShellShock_Log CRITICAL "\"The request was sent from \" +CLIENT.IP.SRC + \" Bash Code Injection Vulnerability\"" -bypassSafetyCheck YES add responder policy ShellShock_policy "HTTP.REQ.FULL_HEADER.REGEX_MATCH(re/\(\)\s*{/) || HTTP.Req.BODY(1000).REGEX_MATCH(re/\(\)\s*{/) || HTTP.REQ.URL.QUERY.REGEX_MATCH(re/\(\)(\s*|\++){/) || HTTP.REQ.BODY(1000).REGEX_MATCH(re#%28%29[+]*%7B#)" DROP ‑logAction ShellShock_Log bind responder global ShellShock_policy 10 END -type REQ_DEFAULT
The following security configurations are detailed by Jason Samuel at Mitigating DDoS and brute force attacks against a Citrix Netscaler Access Gateway:
- Maximum logon attempts on NetScaler Gateway Virtual Server
- Rate Limiting for IP.SRC and HTTP.REQ.URL.
- nstcp_default_XA_XD_profile TCP profile on the NetScaler Gateway Virtual Server.
- Syslog logging
- External website monitoring
- Obfuscate the Server header in the HTTP response
- Disable management access on SNIPs
- Change nsroot strong password, use LDAP authentication, audit local accounts
- Don’t enable Enhanced Authentication Feedback
- SSL – disable SSLv3, deny SSL renegotiation, enable ECDHE ciphers, disable RC4 ciphers. Also see Anton van Pelt Make your NetScaler SSL VIPs more secure (Updated) .
- 2-factor authentication
- Command Center and Insight Center
- Review IPS/IDS & Firewall logs
Management Authentication
Load balancing of authentication servers is strongly recommended since during an authentication attempt only one LDAP server is chosen. If you instead bound multiple LDAP servers it would try all of them and for incorrect passwords will lock out the user sooner than expected.
- Expand System, expand Authentication, and then click LDAP.
- On the right, switch to the Servers tab. Then click Add.
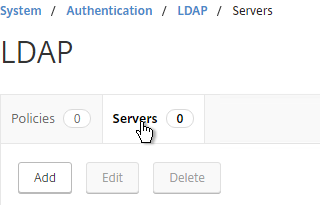
- Enter LDAPS-Corp-Mgmt or similar as the name. If you have multiple domains, you’ll need a separate LDAP Server per domain so make sure you include the domain name. Also, the LDAP policy used for management authentication will be different than the LDAP policy used for NetScaler Gateway.
- Change the selection to Server IP. Enter the VIP of the NetScaler load balancing vServer for LDAP.
- Change the Security Type to SSL.
- Enter 636 as the Port. Scroll down.
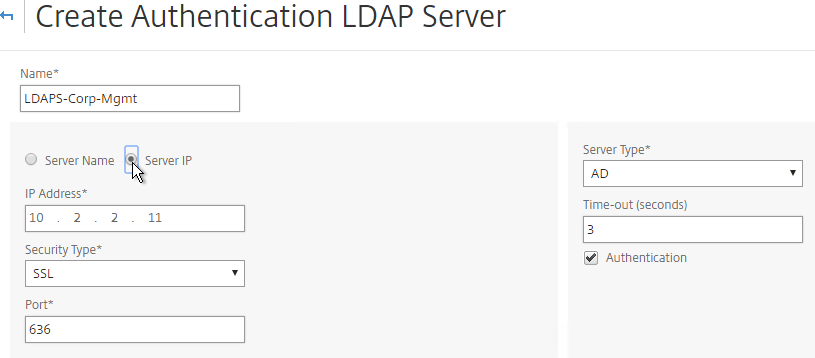
- In the Connection Settings section, enter your Active Directory DNS domain name in LDAP format as the Base DN.
- Enter the credentials of the LDAP bind account in userPrincipalName format.
- Check the box next to BindDN Password and enter the password. Click Test Connection. Scroll down.
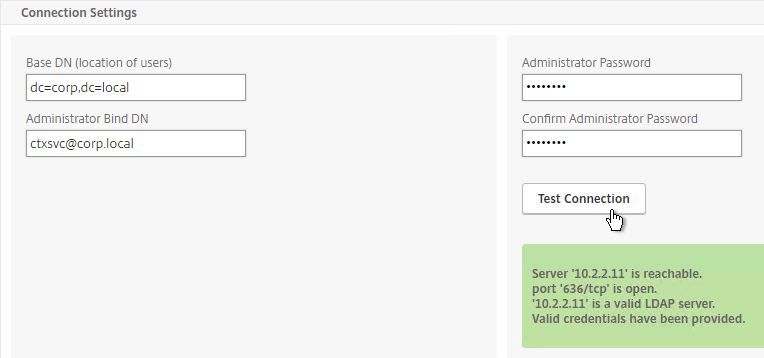
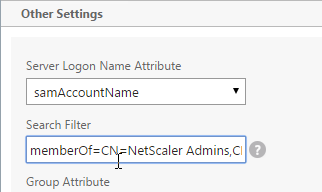
- In the Other Settings section, use the drop-down next to Server Logon Name Attribute, Group Attribute, and Sub Attribute Name to select the default fields for Active Directory.
- On the right, check the box next to Allow Password Change.
- It is best to restrict access to only members of a specific group. In the Search Filter field, enter memberOf=<GroupDN>. See the example below:
memberOf=CN=NetScaler Administrators,OU=Citrix,DC=corp,DC=localYou can add :1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941: to the query so it searches through nested groups. Without this users will need to be direct members of the filtered group.memberOf:1.2.840.113556.1.4.1941:=CN=NetScaler Administrators,OU=Citrix,DC=corp,DC=local
Citrix 132802 How to Use the ldapsearch Utility on the NetScaler Gateway Enterprise Edition Appliance to Validate a Search FilterAn easy way to get the full distinguished name of the group is through Active Directory Administrative Center. Double-click the group object and switch to the Extensions page. On the right, switch to the Attribute Editor tab.Scroll down to distinguishedName, double-click it and then copy it to the clipboard.
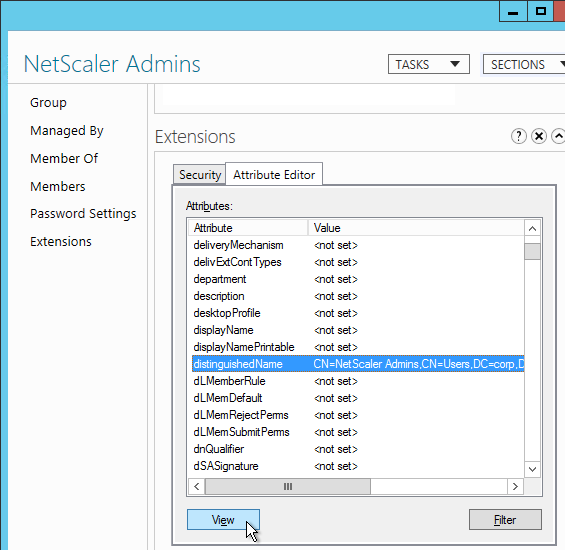
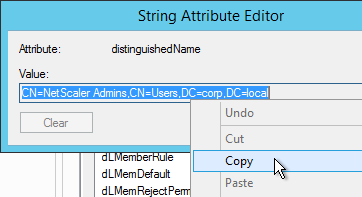 Back on the NetScaler, in the Search Filter field, type in memberOf= and then paste the Distinguished Name right after the equals sign. Don’t worry about spaces.
Back on the NetScaler, in the Search Filter field, type in memberOf= and then paste the Distinguished Name right after the equals sign. Don’t worry about spaces.
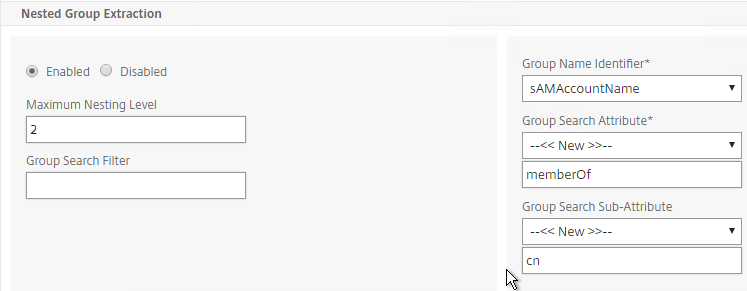
- Scroll down and click More to expand it.
- For Nested Group Extraction, if desired, change the selection to Enabled.
- Set the Group Name Identifier to samAccountName.
- Set Group Search Attribute to –<< New >>– and enter memberOf.
- Set Group Search Sub-Attribute to –<< New >>– and enter CN.
- Example of LDAP Nested Group Search Filter Syntax
- Scroll down and click Create.
add authentication ldapAction Corp-Mgmt -serverIP 10.2.2.210 -serverPort 636 -ldapBase "dc=corp,dc=local" -ldapBindDn "corp\\ctxsvc" -ldapBindDnPassword Passw0rd -ldapLoginName samaccountname -searchFilter "memberOf=CN=NetScaler Admins,CN=Users,DC=corp,DC=local" -groupAttrName memberOf -subAttributeName CN -secType SSL -passwdChange ENABLED
- Switch to the Policies tab and click Add.
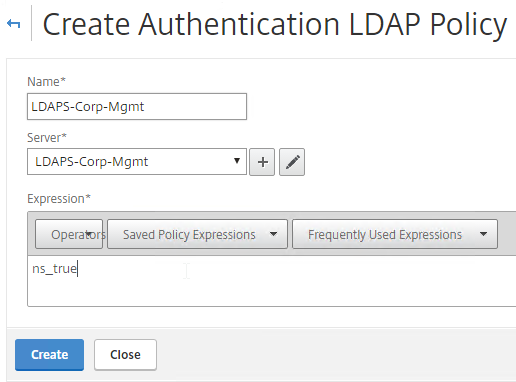
- Enter the name LDAPS-Corp-Mgmt or similar.
- Select the previously created LDAPS-Corp-Mgmt server.
- On the bottom, in the Expressions area, type in ns_true.
- Click Create.
add authentication ldapPolicy Corp-Mgmt ns_true Corp-Mgmt
- Click Global Bindings in the right pane.
- Click where it says Click to select.
- Select the newly created LDAP policy, and click Select.
- Click Bind.
- Click Done.
bind system global Corp-Mgmt
- Under System, expand User Administration and click Groups.
- On the right, click Add.
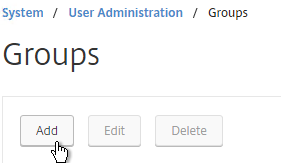
- In the Group Name field, enter the case sensitive name of the Active Directory group containing the NetScaler administrators.
- In the Command Policies section, click Insert.
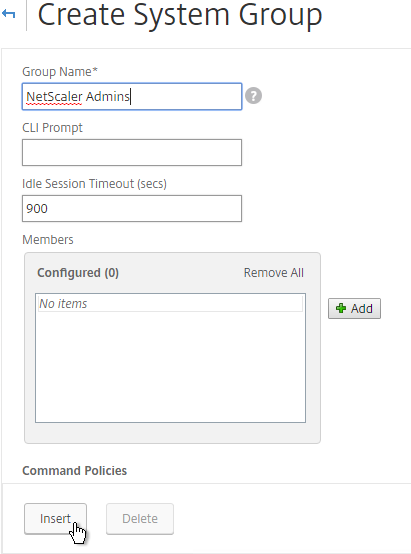
- Select the superuser policy, and click Insert.
- Click Create.
add system group "NetScaler Admins" -timeout 900 bind system group "NetScaler Admins" -policyName superuser 100
- If you logout:
- You should be able to login to NetScaler using an Active Directory account.
CLI Prompt
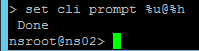
- When you connect to the NetScaler CLI prompt, by default, the prompt is just a
>.

- You can run
set cli prompt %u@%hto make it the same as a UNIX prompt. See Citrix Docs for the cli prompt syntax.
Backup and Restore
- Go to System > Backup and Restore.
- On the right, click the Backup button.
- Give the backup file a name.
- For Level, select Full and click Backup.
- Once the backup is complete, you can download the file.
For a PowerShell script, see John Billekens Create offline backups of the NetScaler config
To restore:
- If you want to restore the system and if the backup file is not currently on the appliance, you click the Backup button. Yes, this seems backwards.
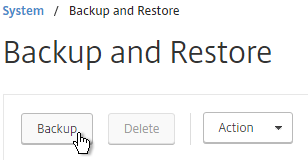
- Change the selection to Add.
- Browse Local to the previously downloaded backup file.
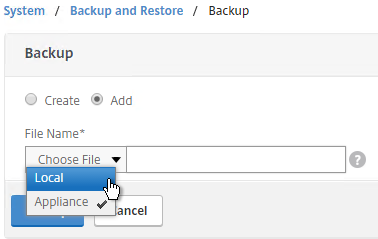
- Then click Backup. This uploads the file to the appliance and adds it to the list of backup files.
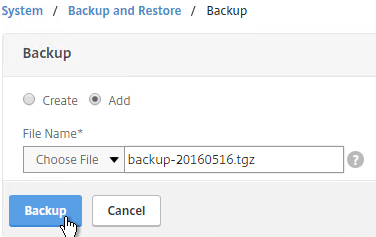
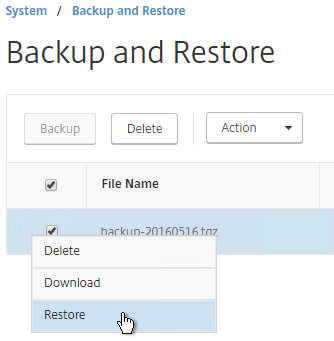
- Now you can select the backup and click Restore.
We have a migration scenario where my web interface, xenapp, Database, netscaler IP’s will change.
Is there any standard procedure that I need to follow while copying over the configuration(ns.conf) from one Netscaler appliance to another appliance. Other servers(web interface/xenapp/database) will be migrated as is and host name will remain same and only IP will change.
It’s easier if you build new appliances, export config from old appliance, and import to new appliance. For ns.conf, edit the file and search/replace the IP addresses. Then you can run the “batch” command to run the file on the new appliance.
One of these days I’ll write a longer procedure to migrate a config from one appliance to another appliance.
Carls,
how can we use SNMP ACL for normal load balance
Hi Carl,
We have a NetScaler 11.1 Build 50.10 HA pair. On the Secondary appliance, some certificate-key pairs are missing but they are present on the primary.
If I compare the files in /nsconfig/ssl folder, the same files (CSR,key,certs) exist on both nodes.
Running HA Sync does not restore the key-pair on secondary. Is it okay to create the key-pair manually on the secondary?
Is the second appliance licensed? Force HA Sync should cause them to be created. Lack of licensing will prevent them from being created.
Thanks Carl!
The secondary appliance shows Enterprise license in GUI and CLI. Does it copy that from primary? How do I check if a separate license file was uploaded to the Secondary.
Under /nsconfig/licenses there are four files on Secondary and two files on Primary NS.
Thanks.
Each appliance is licensed separately, with it’s own files. There’s no replication of licensing.
Look in /nsconfig/ns.conf for “add ssl cerKey” command. Copy one of them to the clipboard and run it in the CLI on the Secondary. What error do you see?
I ran the “add ssl Certkey” command copied from Primary NS. Output was:
ERROR: Resource already exists [certkeyName Contents, <>]
So you’re saying the certKeys are already on the Secondary?
At System > HA, you can do a Force Sync from Primary to Secondary.
It turns out that more than one certificate was requested from a Public CA for the same URL. Both the certificate key pairs existed on the Primary but Secondary would not attach the certificate to vServers.
I had to remove the extra key-pair which was not bound to any vServer from Primary and do an HA Sync. Then, the vServers came UP on Secondary as well.
Thanks a lot for your help!
Dear Carl ,
Seeking your valuable advise on the below scenario.
***************************************************
The end user set up contains two Netscaler appliance ( NSMPX-8005-10G 4*CPU+6*E1K+2*IX+1*E1K) and while doing the health check we found that there is only one NIC in use and all the traffic is going through the same interface which is not the best practise.We have critical servers (XenApp,XenMobile) configurations running inside Netscaler.
Here how can we configure the below requirements without any fail
–Interface Redundancy without affecting the production site
–VLAN Seggregation (Outside Internet VLAN—Management VLAN—Inside Server VLAN)
****************************************************
Please share me your valuable thoughts .
Reconfigure the secondary, failover, then reconfigure the primary. But even that is risky since you can’t test anything until after the failover.
I have a section on dedicated management network – https://www.carlstalhood.com/netscaler-12-system-configuration/#dedicatedmgmt
With both Outside and Inside connectivity, by default, traffic will come in from Outside, and exit from Inside. That means the firewall is bypassed. Are you OK with that?
Yes ,I am OK with the above scenario.
Hi Carl , Please let me know if I can share you the details in private.
Hi I did a backup full but when I do a restore he dont restore all my vips, services, vserver…
how can I backup all this items
If you open the backup file, you can navigate to /nsconfig to find the ns.conf file. Then you can “batch import” it. Make sure the certificates are already loaded in /nsconfig/ssl. And make sure the appliance is licensed (/nsconfig/license).
Hello Carl,
I have an issue with the AD authentication for the Management;
Iam in Netscaler 11.1 55.13 with standard edition
I created Load Balancing for AD and it works. and the authentication for the Gateway works too
I would like link my AD with netscaler just to connect on the console
To see System / Authentication Adavnced Policies / Policy I must to check show unlincensed feature.
I can create A Policy but when i want bind it in Global Policy but nothing it hapenning.(With command it is the same)
I have to buy a platinium license for AAA just to activate this feature?
Thank you for your help
I think it’s fixed in 11.1 build 56 – If you configure an external authentication server, such as RADIUS, by using the NetScaler GUI, the option to bind a classic authentication policy to a system global entity fails. https://docs.citrix.com/content/dam/docs/en-us/netscaler/11-1/downloads/release-notes-11-1-56-15.html
Hello Carl
Thank you for the answer.
I do not use Radius just LDAP.
I will try to upgrade version in build 56 and I give you the return .
PS : Good job for your blog, it is my cmdb for Citrix 🙂
So the build 56 fix this issue.
Thank for your help 😉
Hi Carl
I have deployed netscaler 11 in vmware enviroment and have added another NIC to netscaler for internal network back end connection to the Xenapp servers and storefront. virtual gateway NIC is located in Dmz for external access and its associated with netscaler test certificate, netscaler VIP shows down with red mark .
Would you please help on this issue.
Best Regards
Basem
VIPs are usually down because the bound Service/ServiceGroup is down.
Did you follow my NetScaler VLAN instructions?
If you edit your Service, right-click the member, and click Monitor Details, what do you see?
Insightful article,
Hi Carl, Can I do any in-place upgrade from 10.5 to 11.1?
or
Do I have to upgrade to 11.0 first?
thank you.
Every update is cumulative so you can go directly to the new release. If you have custom theme configured, you’ll have to re-configure it using Portal Themes in 11.1.
Hi Carl, would you recommend going to VMware 6.5 for NS 11.1 VPX even though not yet supported by Citrix? Would keeping it at hw ver 11 make a difference?
Great article. Regarding IP addresses. I understand that the source IP of loadbalanced traffic will be the SNIP IP. However I have a use case where I need the source IP to be the SNIP by default and for a certain LB service be a different IP although on the same subnet.
I’ve read a lot about multiple SNIPs in same subnet, SNIP and MIP coexistance and traffic policies, but what is the correct way to configure this making sure default source IP remains the SNIP and only this one service is changed.
(I can elaborate that this is in regards to some Exchange receive connector shenanigans where I need the source to be different based on the load balancer hit)
https://discussions.citrix.com/topic/387333-different-source-ip-for-specific-lb-service/
Hi Carl, I have configured LDAP authentication for management on our Netscaler VPX. I would like to use UPN style login for this and configured userPrincipalName on the LDAP server. It does not seem to work. LDAP request are being sent to an internal LDAP load balancer. Do you know if this is possible? Thanks!
When I change the LDAP policy/server, Server Logon Name Attribute, to userPrincipalName, I can login with a UPN.
Carl,
We are trying to setup a 2 NetScalers in our DMZ. have a management VLAN and a Data VLAN separated by a firewall. When I go to create the instance it creates it fine, but it evidently cannot reach the data VLAN gateway and blanks it out.
How does the NetScaler do the check, it’s not a ping that we can see. If I try to change it after the instance is created I get the typical:
ERROR: The gateway is not directly reachable
and it fails to change.
Networking is telling us everything is fine. What is can it be, or what needs to be set correctly.
SDX 11.0-64 and higher builds have a Next Hop for Management field when editing an instance. So if management is on a dedicated mgmt network, but default gateway is on the data network, then you use the next hop field with a router on the mgmt network so SDX can communicate with the instance.
Hi Karl, I am setting up Netscaler 11.1 in a lab at home and have configured it for HA but having problems with DNS it shows up as Down. I have looked everywhere for a reason but can’t find anything.
I have enabled SNIP pointing the SNIP address to my default gateway, I am assuming that the reason for this is because I have a single subnet and the Netscaler is in the same subnet as my internal LAN.
Can you shed some light on this for me
Can the NetScaler ping the DNS server?
Any Chance of including, How to configure NetScaler Logs using Splunk
Carl just a quick question on the two arm setup. When we downloaded the latest 11.1 OVF and started the install on the network configuration setup it only offered one NIC. We have obviously added another one, in fact we added two as we would like to split out management traffic. Is this a design change in the Netscaler setup or just a mistake in the OVF?
Thanks
SV
I believe they did make this change in 11.1 but I’m not certain.
Carl,
Thanks for that. One more question as I am confused.
We have installed 11.1 on a new netscaler, We then added 2 more Nics (1, management; 2, DMZ; 3, Internal) We are using this device for multi tenancy so the 3rd nic is doing tagging on multiple VLANS. This is working in our HK DC on the older version of VPX and we are not using the management nic.
Now we have this deice up and running and everything is stating up and enabled. however we can ping the VIP but when browsing to it we get the site cannot be reached. We have done a lot of these setups recently and not had an issue so thought you might have some ideas especially as there have been some changes since 11. We got caught out forgetting to enable the feature for security (Just an example)
Is the NetScaler using SSL to communicate with the back-end server? I’m hearing that TLS issues have returned in 11.1.
This is just insane how fast you are.
Thank You Charl , Any idea if the update to 11.1 is supported on MS Azure?
I have not tried it on Azure. But in theory, all recent builds should work.
Hello Carl:
I have been trying to save changes to rc.netscaler file, however it resets after few minutes to its original state, I made sure I have permissions to the file. After saving changes it looks good for just 1 min or so and then goes back to old state, I’m using NetScaler 11.1, no custom scripts that I can see here
Are you changing it on the Primary appliance and not the Secondary?
Yes, that was it looks like I was doing it on Secondary appliance. Why does it block it anyway on the secondary appliance?
Thanks
Actually, the primary was replicating over the secondary.